Natawidjaja, D. H., Daryono, M. R., Prasetya, G., Udrekh, Liu, P. L., Hananto, N. D., Kongko, W., Triyoso, W., Puji, A. R., Meilano, I., Gunawan, E., Supendi, P., Pamumpuni, A., Irsyam, M., Faizal, L., Hidayati, S., Sapiie, B., Kusuma, M. A. and Tawil, S.,
Geophysical Journal International (Q1)
2020
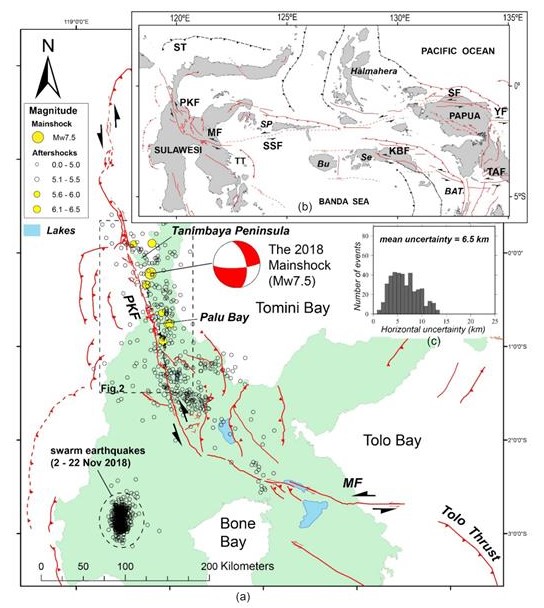
On 2018 September 28, 18:02:44 local time, the magnitude 7.5 earthquake accompanied by a tsunami and massive liquefaction devastated Palu region in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Comprehensive post-disaster surveys have been conducted, including field survey of surface ruptures, LiDAR, multibeam-bathymetry mapping and seismic-reflection survey. We used these data to map fault ruptures and measure offsets accurately. In contrast to previous remote-sensing studies, suggesting that the earthquake broke an immature, hidden-unknown fault inland, our research shows that it occurred on the mappable, mature geological fault line offshore. The quake ruptured 177-km long multifault segments, bypassing two large releasing bends (first offshore and second inland). The rupture onset occurred at a large fault discontinuity underwater in a transition zone from regional extensional to compressional tectonic regimes. Then, it propagated southward along the ∼110-km submarine fault line before reaching the west side of Palu City. Hence, its long submarine ruptures might trigger massive underwater landslides and significantly contribute to tsunami generation in Palu Bay. The rupture continued inland for another 67 km, showing predominantly left-lateral strike-slip up to 6 m, accompanied by a 5–10 per cent dip-slip on average. The 7 km sizeable releasing bend results in a pull-apart Palu basin. Numerous normal faults occur along the eastern margin. They cut the Quaternary sediments, and some of them ruptured during the 2018 event. Our fault-rupture map on mature straight geological fault lines allows the possible occurrence of early and persistent ‘supershear’, but significant asperities and barriers on segment boundaries may prohibit it.