Pepen Supendi, Andri Dian Nugraha, Sri Widiyantoro, Chalid Idham Abdullah, Nanang T. Puspito, Kadek Hendrawan Palgunadi, D. Daryono, Samsul Hadi Wiyono
Geoscience Letters (Q1)
16 Desember 2019
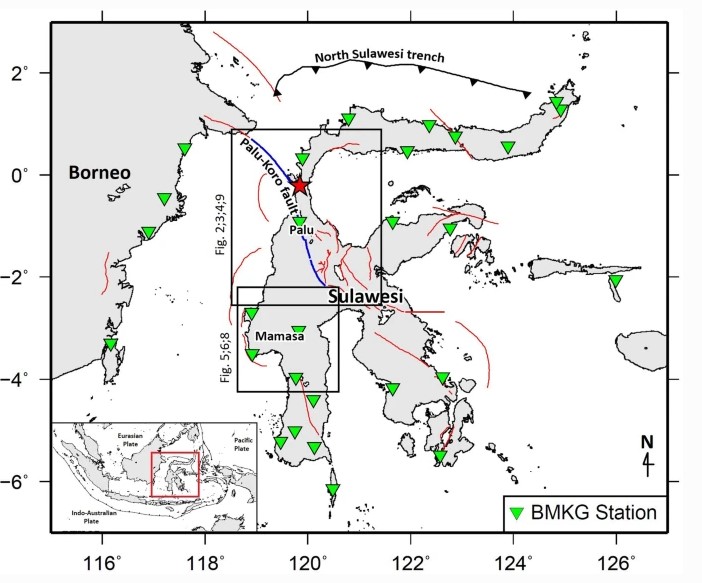
On September 28, 2018, the Mw 7.5 earthquake occurred in Palu, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. This earthquake produced strong tremors, landslides, liquefaction and a tsunami and caused thousands of fatalities and damaged houses and infrastructure. We have relocated 386 of the 554 Palu aftershocks by using the double-difference relocation method (hypoDD) from September 28 to November 22, 2018. The aftershock pattern is consistent with the crustal deformation in the area and generally shows that the events have a NW–SE trending of ~ 200 km in length and ~ 50 km in width. Most of the aftershocks are located to the east of the Palu-Koro Fault Line. Since November 2, 2018, there have been hundreds of swarm earthquakes in the area of Mamasa, West Sulawesi, which is about 230 km south of the city of Palu. Some of these earthquakes were felt, and houses were even damaged. We have relocated 535 of the 556 swarm earthquakes having a magnitude of M 2 to M 5.4. Our results show that the seismicity pattern has a dip that becomes shallower to the west (dipping at a ~ 45° angle) and extends from north to south for a length of ~ 50 km. We also conducted a focal mechanism analysis to estimate the type of fault slip for selected events of an M > 4.5 magnitude. Most of the solutions of the focal mechanism analysis show a normal fault type. This swarm earthquake probably corresponds to the activity of the fault in the local area.